

A 67-year-old man with a history of oral lesions for at least 1 year presented for evaluation. He complained of “white” lesions, primarily on his buccal mucosa, that were symptomatic; i.e., he experienced burning sensations at rest and during mastication.
The GI tract is essentially a tube extending from the oral cavity to the anus. This tube is organized into a series of four distinct layers which are fairly consistent throughout its …
Premalignant Oral Lesions. A routine part of an oral examination should be inspection not only of the teeth and gums but also of the soft tissues in and around the mouth.

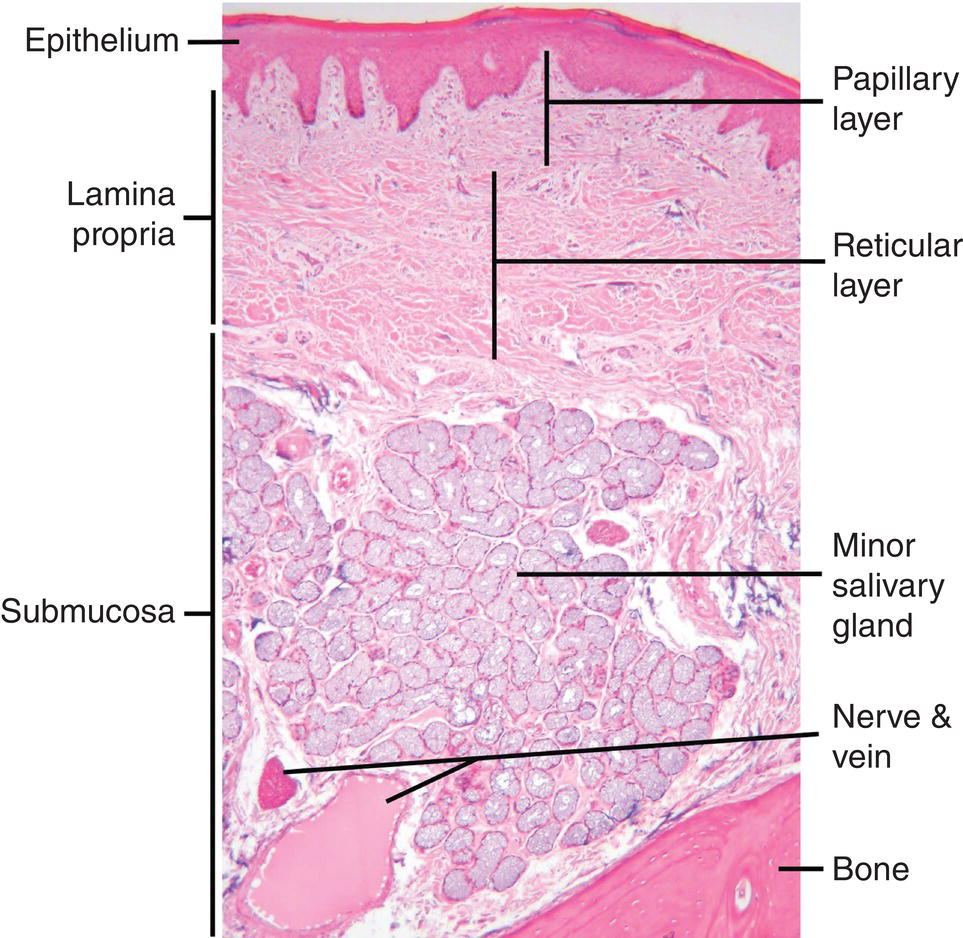
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria.
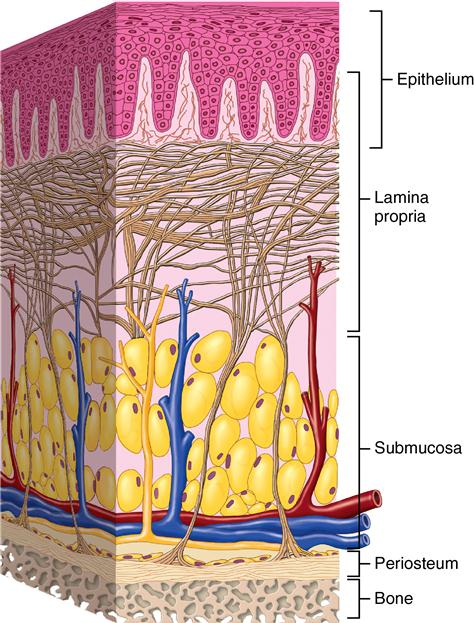
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue.
Various mucosal abnormalities can be identified in the posterior oral cavity and oropharynx. It is not uncommon for individuals to identify lesions and bring it to the attention of their dentist.
Pictures and nasal photos of diseasese involving the nose, including polyps, cancers, rhynophyma, septal hematomas, saddle deformity, septal spurs, papillomas, tumors, and other nasal lesions.
Definition Leukoplakia is a clinical term, and the lesion is defined as a white patch or plaque, firmly attached to the oral mucosa, that …

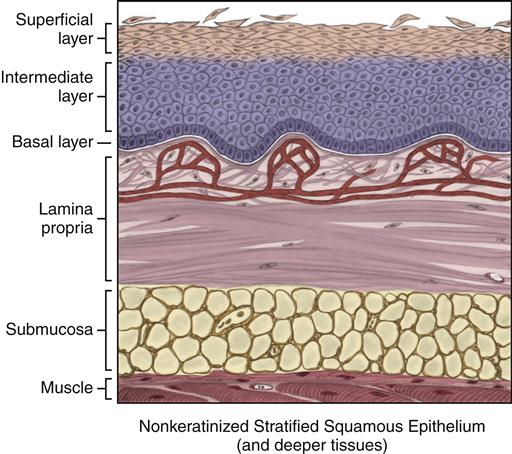

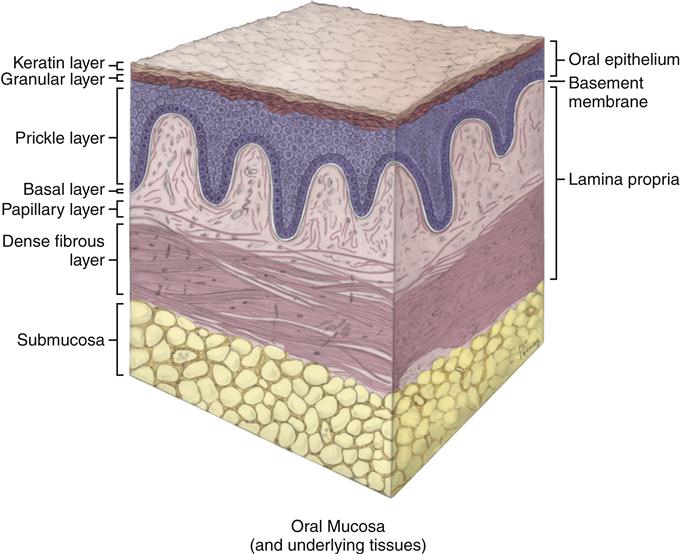
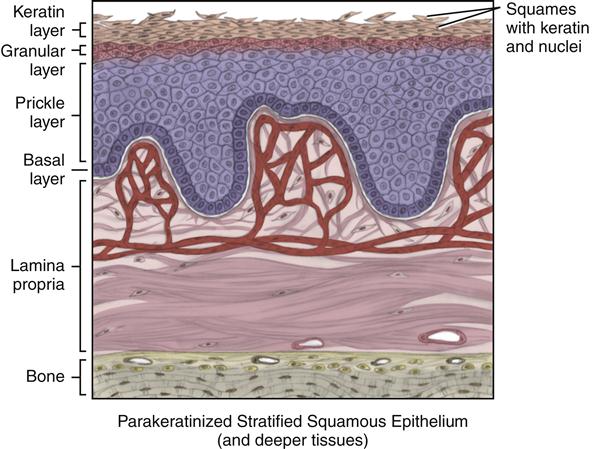
The oral mucosa or “skin” inside the mouth covers most of the oral cavity apart from the teeth. It acts as a barrier and protects the deeper tissues.
Primary lesions of Oral Cavity: MACULE: Well circumscribed flat lesions that are noticeable due to the change in color of Skin or Mucosa. Red- Inflamation